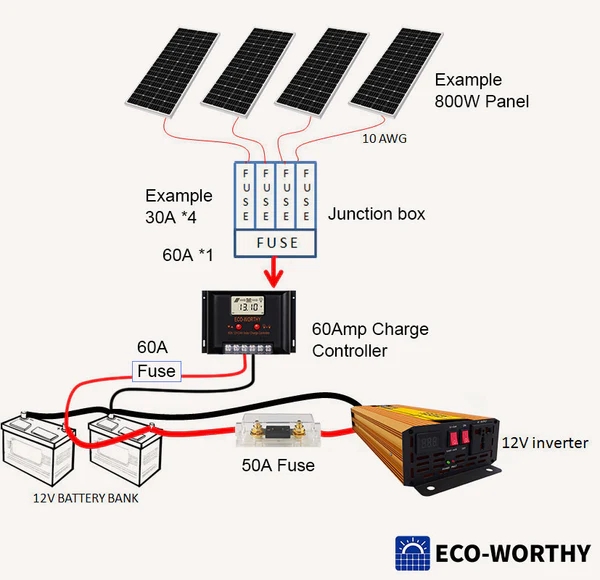
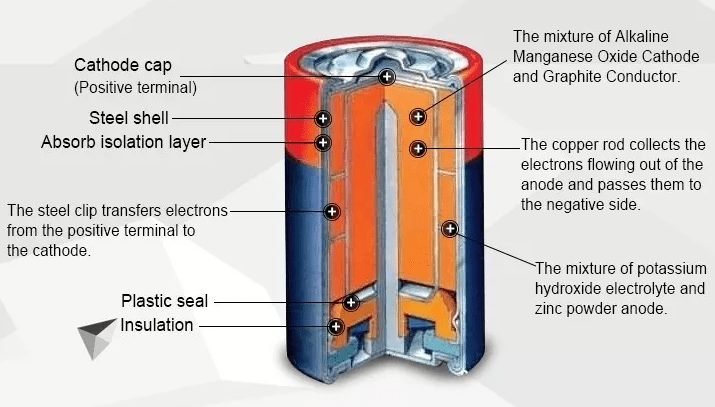
The shift to renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power opens up exciting possibilities for giving the planet a cleaner future. However, these energy sources have a well-known challenge - inconsistency. That's where energy storage comes in, playing a vital role in bridging the gap between energy production and consumption.
Lithium-ion batteries are at the forefront of energy storage solutions, with lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, also known as LFP batteries, rising rapidly. Let's take a closer look at the promising future of Lifepo4 batteries and explore their use cases in energy storage.
Why are Lifepo4 batteries poised for success?
Lifepo4 batteries offer several advantages that make them ideal for energy storage applications:
Safety: One of its biggest advantages is its inherent stability. Unlike some other lithium-ion battery types, Lifepo4 batteries are less susceptible to thermal runaway, a dangerous condition that can lead to fire. This makes them a safer choice for large-scale energy storage systems.
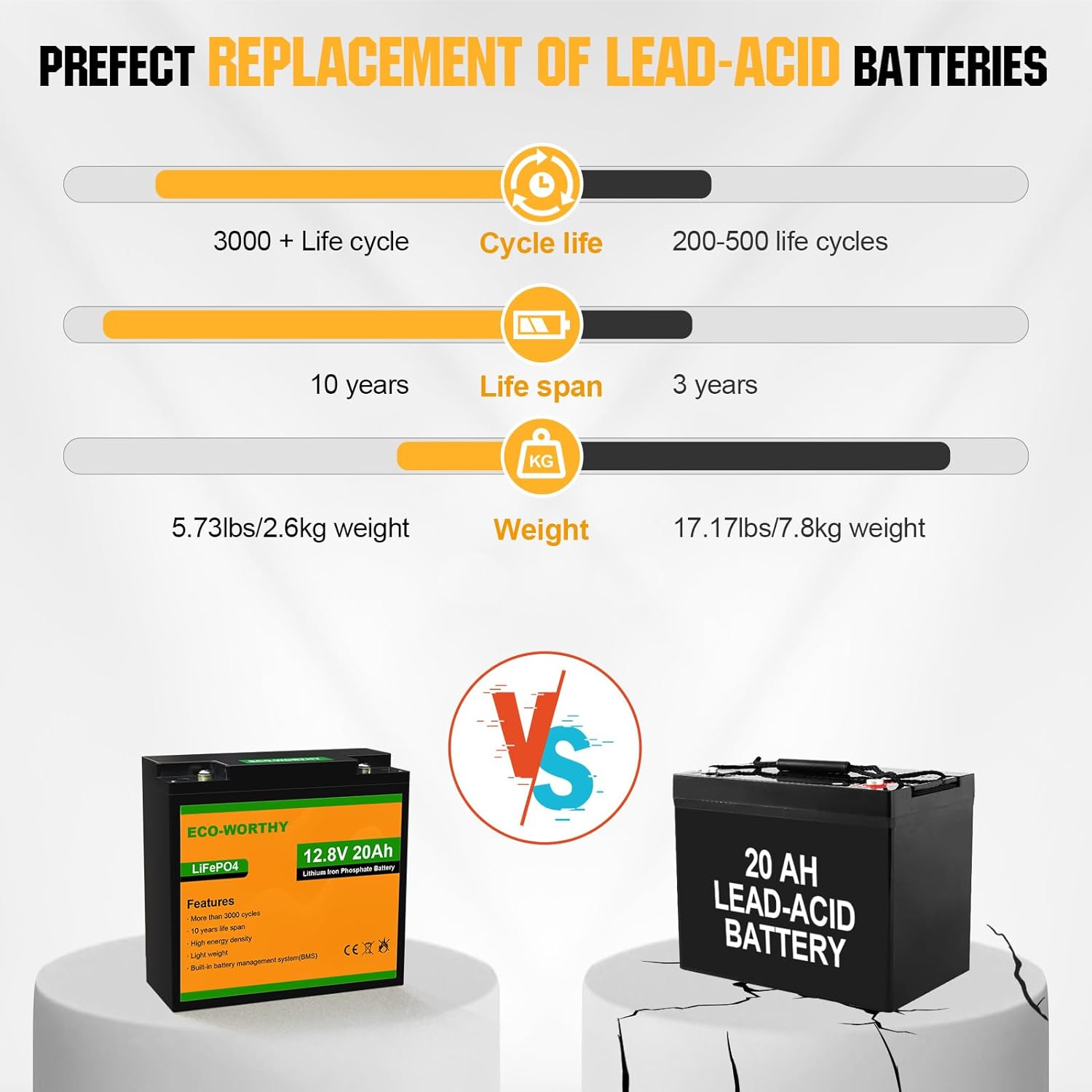
Long Cycle Life: Lifepo4 batteries have an extremely long cycle life, which means they can go through a large number of charge/discharge cycles before losing capacity. In the long run, this means longer life and lower replacement costs.
High Power Density: Lifepo4 batteries provide high power output, making them ideal for applications that require a quick burst of energy, such as grid balancing or electric vehicle charging stations.
Wide Temperature Resistance: These batteries perform well over a wider temperature range than other lithium-ion batteries. This is critical for regions with extreme climatic conditions.
Conclusion
Lifepo4 batteries are revolutionizing the energy storage sector. Their inherent safety, long lifespan and wide range of applications make them an ideal solution for integrating renewable energy, improving grid stability and powering a sustainable future. As research and development continues, we can expect Lifepo4 batteries to become even more efficient and cost-effective, further solidifying their importance in energy storage.
...